Recently, team of Professor Zhanshan Wang and Professor Xinbin Cheng from IPOE proposed a comprehensive performance domain tolerance methodology and successfully developed a prototype for freeform image spectrometers. The results were published in Optics Express with the title “Comprehensive performance domain tolerance analysis methodology for freeform imaging spectrometers”.
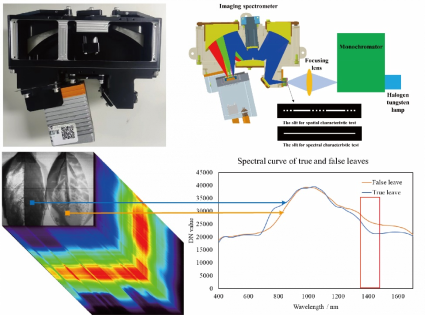
Imaging spectrometers, integral for simultaneous acquisition of spatial and spectral data, have become indispensable in a multitude of domains, such as earth observation, deep space exploration, intelligent agriculture, food safety inspection, criminal detection, and biomedical measurement. the spectral imaging system based on freeform surfaces and plane gratings demonstrates cost-effectiveness, high performance, lightweight characteristics, as well as miniaturization potential, rendering it a prominent focus in current research endeavors. Conventional tolerance analysis methods often rely solely on the modulation transfer function (MTF) criterion. However, for a spectrometer system, factors such as the keystone/smile distortion and spectral resolution performance also require consideration.
In this work, the team propose a comprehensive performance domain tolerance analysis method for freeform imaging spectrometers, encompassing exhaustive tolerance criteria such as the system MTF, keystone/smile distortion, and spectral resolution. These tolerance criteria were evaluated by performing conjoint calculations in Zemax and Matlab based on performance rendering, as illustrated in Figure 1. This approach consists of four key components: tolerance parametric model unit, comprehensive performance evaluation unit, sensitivity analysis unit, and tolerance values adjustment unit.
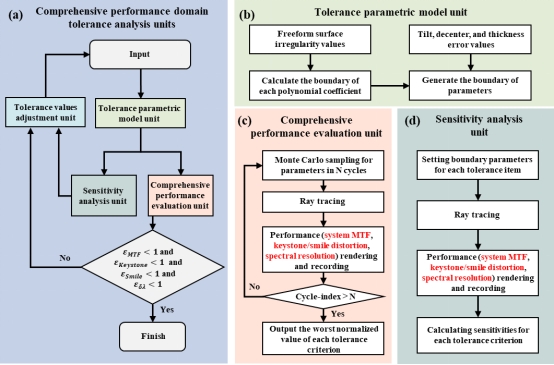
Figure 1. Framework of the comprehensive performance domain tolerance analysis method for freeform imaging spectrometer.
Based on the comprehensive performance domain tolerance analysis method, we conducted the tolerance analysis of a freeform imaging spectrometer. The tolerance analysis results identified the first (M1) and third (M3) freeform mirrors as critical components. To improve the assembly efficiency, we developed and implemented a preassembly process for these mirrors by utilizing a computer-generated hologram (CGH) for alignment purposes. Subsequent assembly and rigorous performance evaluation of the spectrometer confirmed the effectiveness of our comprehensive performance domain tolerance analysis method, as shown in Figure 2.
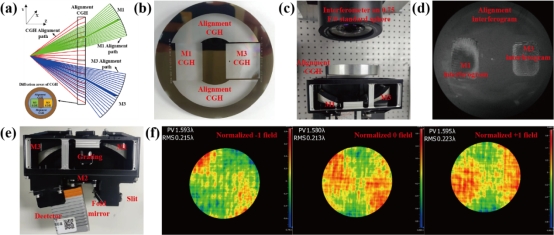
Figure 2. The development of a prototype for freeform image spectrometer
This work offers valuable recommendations for the advancement of freeform image spectrometer. The developed prototype exhibits exceptional imaging capabilities and has been subjected to exploratory experiments in the field of camouflage identification applications, as depicted in Figure 3.
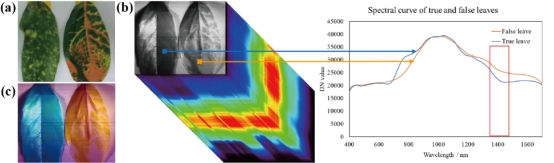
Figure 3. Application for the identification of true and false leaves.
Professor Xiong Dun (from Tongji University) is the corresponding authors of the paper. Yujie Xing (doctoral candidate at Tongji University) and Jun Yu (assistant professor) are co-first authors of the paper. Collaborators with outstanding contributions to the paper also include Professor Zhanshan Wang (from Tongji University), Xinbin Cheng (from Tongji University), Dongfang Wang (from Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences), Xuquan Wang(postdoctoral fellow from Tongji University), Zhiyuan Ma (doctoral candidate at Tongji University), Chunling He (doctoral candidate at Tongji University), and Hongmei Li (engineer at Tongji University).
Information of the paper:
Yujie Xing, Jun Yu, Xuquan Wang, Hongmei Li, Zhiyuan Ma, Chunling He, Dongfang Wang, Xinbin Cheng, Zhanshan Wang, Xiong Dun. “Comprehensive performance domain tolerance analysis methodology for freeform imaging spectrometers”. Optics Express, 2024, 32(8): 14405-14419.
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.519818
